With any type of business, there are inevitably costs involved in day-to-day operations. These costs need to be accounted for to determine the profitability of a business. Trading in the forex market also has costs that beginner traders need to be aware of and account for before they start trading.
Although there are many types of costs that businesses outside of the trading space have to deal with on a daily basis, a retail trader’s main cost is the commission.
Just like you would have to pay a fee for exchanging your country’s currency for a foreign currency at an airport exchange kiosk, for example, you will be charged a commission for executing trades in the forex market via your trading platform and broker.
The purpose of this article is to explain what a forex commission is, and the various types of commissions that forex brokers charge, so that you are aware of these fees and account for them when trading the forex market.
FOREX COMMISSION EXPLAINED
Before we discuss what a forex commission is, we first need to define the two parties that are involved when it comes to transacting in the forex market.
The first party involved in a forex trading transaction is you, the retail trader. A retail trader is simply defined as an individual trader who speculates with their own money for personal gain and does not trade on behalf of an institution.
The second party involved in a forex transaction is your broker. A retail forex broker essentially provides a trader with access to a platform for the sole purpose of buying and selling foreign currencies for speculative purposes. Forex brokers therefore act as the middleman between you, the retail trader, and the forex market.
Another Information
The fees that brokers charge in order for you to trade the currency market are referred to as the forex commission. Without a broker, a retail trader will have no way to trade the foreign exchange market, which is why brokers charge commissions for providing access and the convenience to participate in currency trading.
The forex commission is automatically deducted from your trading equity when placing trades via your trading platform, but knowing upfront how much these costs are is an important consideration that might impact your particular trading style.
For example, scalpers generally execute multiple trades a day and will have to make sure that the commissions they pay do not eat into the profitability of this style of trading. It would therefore make sense that a scalper chooses a broker that offers very small commissions.
Swing traders, on the other hand, will typically hold their positions anywhere from a few days to several weeks and will likely be less worried by trading commissions as they trade less frequently.
In the end, forex commissions can be compared to your business ‘overheads’, so be sure to factor in these costs when determining your overall strategy.
TYPES OF FOREX COMMISSION
Before we take a closer look at the different forex commission types that brokers may charge, we first need to recap what a spread is. The spread refers to the difference between the bid and ask price of a forex pair.
Let’s say that you see the following quote on your trading platform: ‘EUR/USD – 1.0525 – 1.0527.’ The difference between the two quotes (the bid and ask price) represents the spread, which in this example will be two pips.
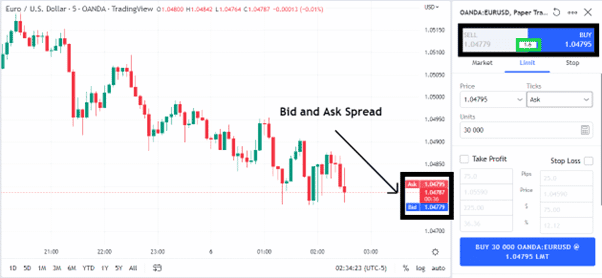
(Image for illustration purposes only)
The bid and ask spread are the two quotes provided by your broker for selling or buying a currency pair. The chart image above shows the quoted bid and ask prices for the EUR/USD forex pair on the price scale, and in the order window on the far right.
In this example, the difference between the bid and ask prices was 1.6 pips, as marked with the green box in the order window.
Forex brokers make their money by either charging a commission or a spread for each trade in return for executing your buy and sell orders.
Not all forex brokers have the same commission structure and can charge their fees in one of three ways: a fixed spread, a variable spread, or a commission based on a percentage of the spread.
FIX SPREAD
A fixed spread is the simplest type of forex commission to understand. The broker quotes a bid and ask price for a currency pair, and its commission is the difference between those two prices. For example, if the EUR/USD bid price is 1.1050 and the ask price is 1.1051, the spread would be 1 pip and the broker’s commission would be $0.10 (1 pip x $0.10 per pip).
A variable spread is similar to a fixed spread, but the bid and ask prices can vary depending on market conditions. For example, if the EUR/GBP bid price is 0.8590 and the ask price is 0.8591 in normal market conditions, but spikes to 0.8650 and 0.8660 during a period of high volatility, the spread would be 10 pips and the broker’s commission would be $1 (10 pips x $0.10 per pip).
The third type of forex commission is based on a percentage of the total trade value. For example, if you’re buying €100,000 worth of EUR/USD at 1.1000 with a 0.1% commission rate, then your broker’s commission would be €100 (100,000 euros x 0.001).
Please note that the above commission amounts were used for explanation purposes only and can vary from broker to broker.
ADDITIONAL FEES
Some forex brokers may also charge additional fees such as account maintenance, payment processing for depositing or withdrawing funds, account inactivity, margin calls, etc.
While some forex brokers may charge for some or all of the above mentioned fees, others may not charge these fees at all. Always check the ‘small print’ with regard to broker fees and forex commission before you sign up and start trading.
CONCLUSION
Regardless of which commission structure a broker uses, forex commission can be seen as the cost of doing ‘business’ and should be factored into your overall trading strategy.
When it comes to forex commission, it is advisable that a novice trader takes the time to research different brokers so that the commissions and/or additional fees are known before opening a forex trading account.
Not all brokers are created equal, which is why it is best to sign up with a reputable and regulated broker. Should anything be unclear with regard to a broker’s exact commission structure and fees, reach out to its support team for clarity. This way, you should be able to avoid any nasty surprises.

